Introduction
Renishaw caters to various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and electronics, as mentioned by Leonard, (2024). Their product lineup addresses diverse needs with precision tools like metrology fixtures, CMM probes, and machine calibration systems for manufacturing. In position measurement, they offer magnetic and optical encoders, while their additive manufacturing systems support research and production, enabling innovation across industries.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Kelley, (2024) explains that machines designed to think, learn, and make decisions independently simulate human intelligence, which we call Artificial Intelligence (AI). It encompasses a range of technologies and methods that enable computers to process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and solve complex problems without being explicitly programmed for every task. By mimicking human cognitive functions such as perception, reasoning, and adaptability, AI allows machines to understand natural language, interact with their environment, and respond to changing circumstances. Far from being just a concept in science fiction, AI is now an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing industries like healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment while shaping the future of how we live and work.
Key Abilities of AI
Shabbir & Anwer, (2018) define the following key stages.
- Computer Vision: AI analyzes and interprets visual data from the environment, enabling tasks like facial recognition and image processing.
- Speech Recognition and Synthesis: AI converts spoken language into text and vice versa, enabling virtual assistants and voice interfaces.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI understands, interprets, and generates human language, facilitating chatbots, translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Knowledge Representation: AI organizes and structures information to simulate human-like understanding and reasoning.
- Reasoning: AI applies logic to conclude, solve problems, and make decisions based on available data.
- Planning: AI develops strategies and actions to achieve specific goals, optimizing efficiency and outcomes.
The image below visually represents the abilities of AI.
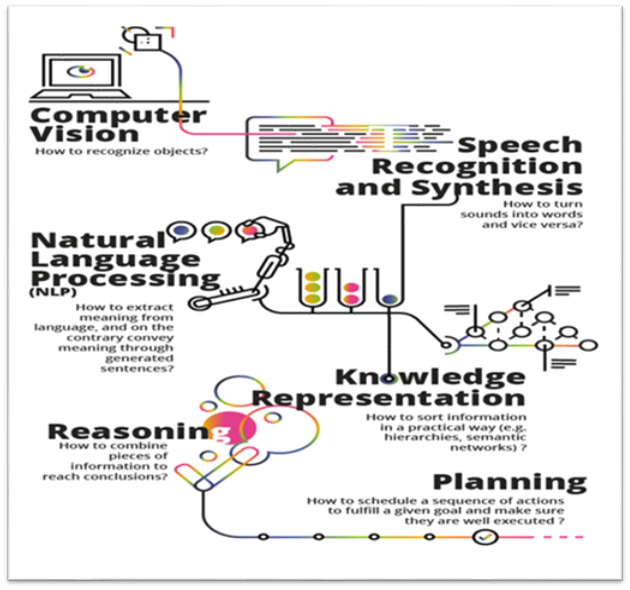
Figure 1: Abilities of Artificial Intelligence
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Glover, (2024) highlights that Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous advantages, making it an invaluable tool across industries. It automates repetitive tasks like data entry, factory operations, and customer service, freeing human resources for higher-priority activities. Its capacity to process large datasets enables AI to solve complex problems, such as predicting financial trends or optimizing energy solutions, with speed and accuracy. AI enhances customer experiences through personalized interactions, chatbots, and self-service tools, improving satisfaction and retention. In healthcare, AI accelerates diagnoses, aids in drug discovery, and facilitates the use of medical robots, revolutionizing patient care. Additionally, its ability to detect patterns and anomalies in data significantly reduces human error, ensuring precision and reliability in various applications.
Potential Issues with Artificial Intelligence
Lumenalta, (2024) discusses how Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents several challenges despite its transformative potential. Issues such as lack of transparency in decision-making (“black box” problem), data privacy concerns, and bias in AI models raise trust and ethical questions. The high demand for AI skills and difficulty integrating AI with legacy systems further complicate adoption. Additionally, the high costs of implementation, especially for small businesses, and growing ethical concerns around AI usage highlight the need for responsible practices. Addressing these challenges requires investments in explainable AI, robust privacy measures, bias mitigation strategies, upskilling programs, hybrid integration models, and ethical AI frameworks.
Renishaw – An Overview of Products and an Insight into the Application of AI Technology and Challenges
Precision Products for Modern Industries
Leonard, (2024) explains that the portfolio of precision products spans industrial metrology, position measurement, and additive manufacturing, offering solutions that address the demands of various industries. These innovations, from style for probes to automated gauging systems, enable high accuracy and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Additionally, advanced tools in additive manufacturing pave the way for creating complex components with reduced material waste.
AI’s Role in Enhancing Product Capabilities
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force in product development and application, according to Leonard, (2024). By integrating AI into industrial tools, real-time monitoring and predictive analytics are achieved, significantly improving operational reliability. AI-enabled systems optimize production lines by reducing errors, enhancing accuracy, and maintaining consistency in manufacturing outputs.
Overcoming Challenges in AI Integration
Leonard, (2024) notes that integrating AI into manufacturing and healthcare technologies brings significant challenges. Key issues include ensuring data integrity, managing the complexities of AI algorithms, and addressing cybersecurity risks. Additionally, resistance to adopting AI technologies in traditional industries requires strategic approaches, including education and system adaptability, to facilitate smoother transitions.
Applications in Healthcare Technology
Healthcare technologies are benefiting from AI-driven precision instruments, as observed by Leonard, (2024). Researchers are designing advanced drug delivery systems and neurological devices to improve patient care and treatment accuracy. AI contributes to these innovations by enabling real-time adjustments and predictive insights, fostering advancements in personalized medicine, and enhancing procedural outcomes.
Balancing Innovation with Sustainability
Sustainability is a critical consideration in modern technological advancements, as highlighted by Leonard, (2024). Developers are creating precision products and AI technologies that focus on reducing environmental impact. From energy-efficient manufacturing processes to waste reduction techniques, aligning innovation with sustainability ensures that technological progress supports long-term ecological balance.
Why Adopt Artificial Intelligence?
European Parliament, Directorate General for Parliamentary Research Services., (2020) emphasizes that adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers unparalleled opportunities to revolutionize industries and improve everyday life. In healthcare, AI enhances diagnostics, personalizes treatments, and streamlines operations, while in mobility, it powers safer, more efficient transportation systems. By automating routine tasks, AI boosts productivity and enables humans to focus on creative, strategic endeavors. Its ability to analyze vast data supports better decision-making, helping businesses and governments address complex challenges effectively.
According to the European Parliament, Directorate General for Parliamentary Research Services., (2020), AI adoption is vital for staying competitive in a data-driven world beyond practical benefits. Organizations using AI can optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and address global issues like climate change through more competent resource management. While challenges like bias and privacy concerns exist, the immense opportunities make AI a key driver of innovation and progress.
References
Kelley, K. (2024, January 10). What is Artificial Intelligence? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners – Caltech. Caltech –. https://pg-p.ctme.caltech.edu/blog/ai-ml/what-is-artificial-intelligence
Shabbir, J., & Anwer, T. (2018). Artificial Intelligence and its Role in Near Future (arXiv:1804.01396). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.01396
Glover, E. (2024, December 3). What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Built In. https://builtin.com/artificial-intelligence
Lumenalta. (2024, August 20). 9 AI problems in 2025: Common challenges and solutions. Lumenalta. https://lumenalta.com/insights/ai-problems-9-common-challenges-and-solutions
European Parliament. Directorate General for Parliamentary Research Services. (2020). Artificial intelligence: how does it work, why does it matter, and what we can do about it? Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2861/44572
Leonard, P. (2024). Renishaw – An overview of products and an insight into the application of AI technology and challenges.
